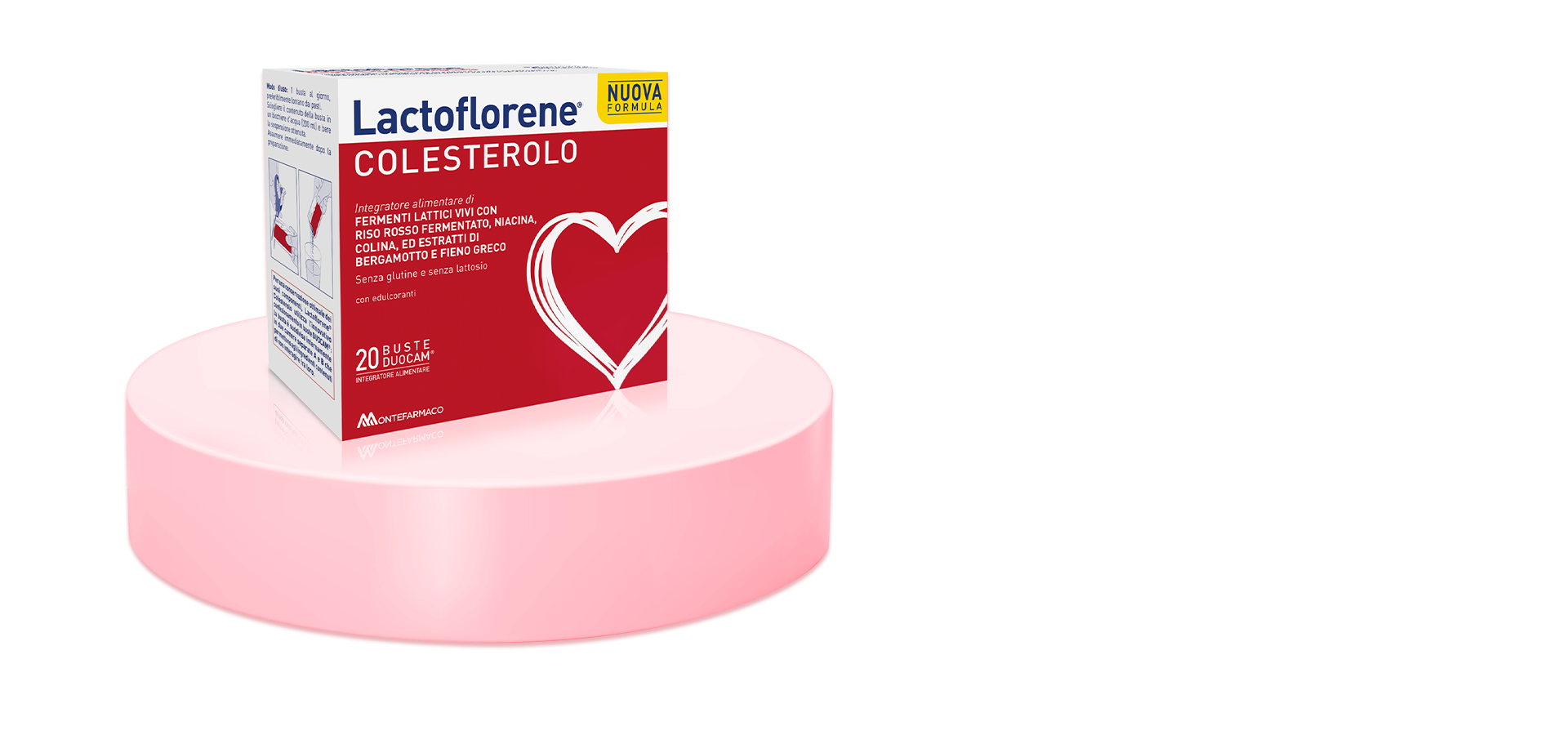
Lactoflorene® Colesterolo, to maintain normal levels of cholesterol in the blood
Lactoflorene® Colesterolo is a food supplement containing probiotics, monacolin from red yeast rice, niacin, choline, bergamot and fenugreek extracts, which help to maintain normal levels of cholesterol in the blood.